Have you heard about the fourth industrial revolution? We’re pretty sure that you may have heard it, but we probably don’t know exactly what it is and what it’s brought to us.
For years we’ve heard about the XIX century’s industrial revolution, and we may have thought that we are in the third revolution, but certainly not. We have moved forward and want to unveil what industry 4.0 is and why it started the fourth revolution.
Please keep reading and find it out.
1. The evolution of the industrial revolutions
As we briefly mentioned, industries have substantially evolved in the last two-and-a-half centuries.
The first revolution began in Britain’s last half of the XVIII century. It introduced us to water and steam power in manufacturing, enabling mass production and evolving from using human and animal power.
Then, the second revolution arrived after passing one-century thanks to oil, gas, and electricity power. It brought the assembly line to the manufacturing process. Hence, it increased productivity and the first level of manufacturing automation thanks to improved communication through telephone and telegrams.
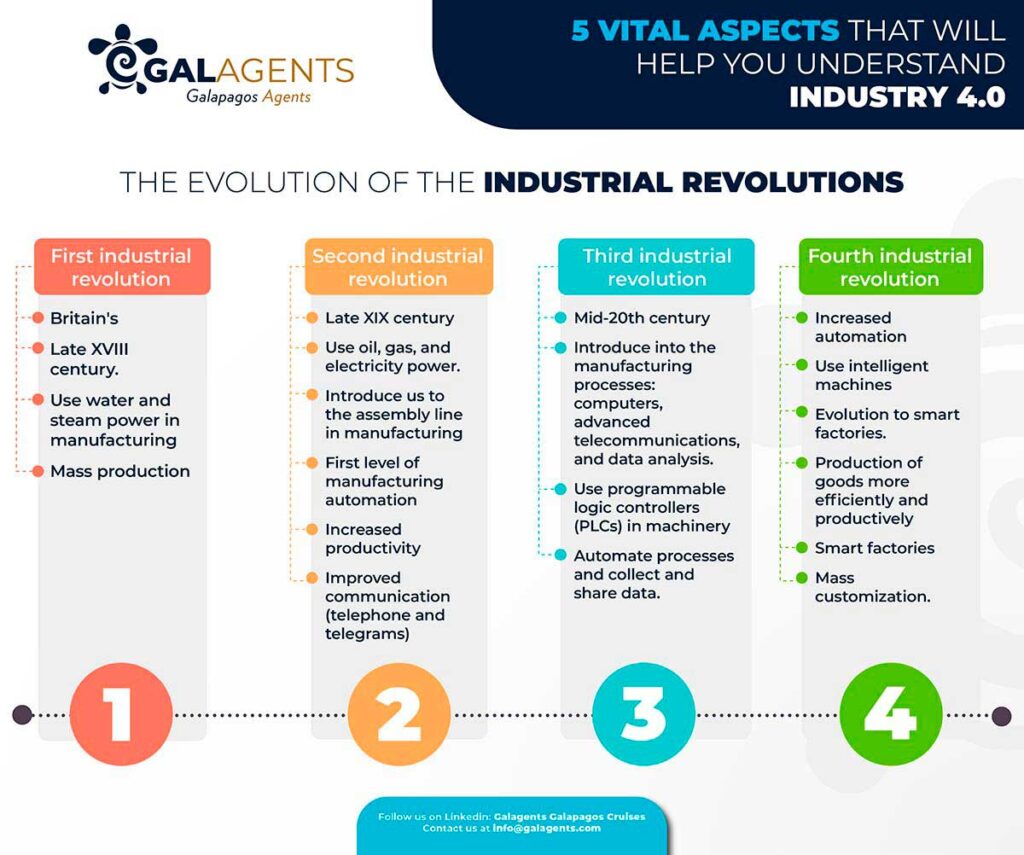
The third revolution appeared in the mid-20th century with the introduction of computers, advanced telecommunications, and data analysis in the manufacturing processes. That was possible due to the use programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in machinery to help automate some processes and collect and share data.
Increasing automation, intelligent machines, and smart factories helped the fourth industrial revolution. Informed data helps to produce goods more efficiently and productively across the value chain. Smart factories make better decisions by collecting more data from the factory and combining that with other enterprise operational data. Moreover, manufacturers can better meet customer demands by using mass customization.
2. What’s Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is the name for manufacturing technologies’ current automation and data exchange trends. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing, and the creation of the smart factory.
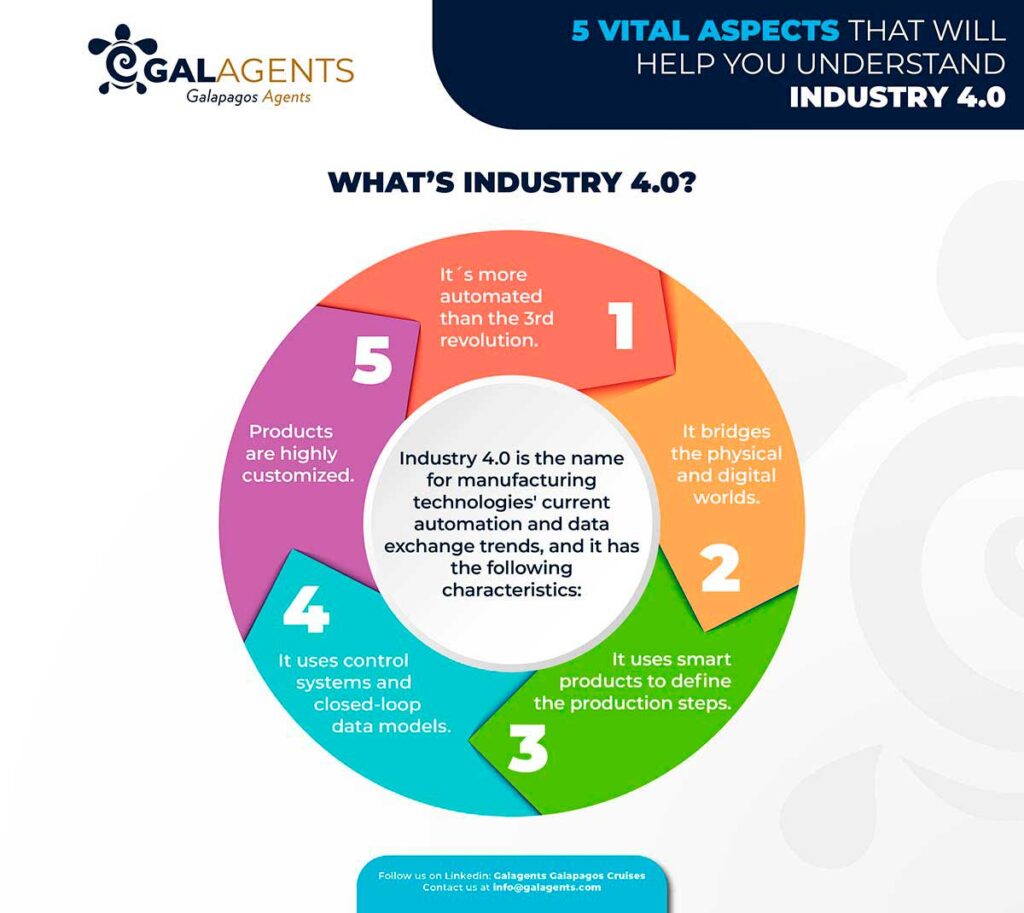
According to I-Scoop, this 4th industrial era has five primary characteristics:
- It’s more automated than in the third industrial revolution.
- It bridges the physical and digital world through cyber-physical systems enabled by Industrial IoT.
- Smart products define the production steps by shifting the central industrial control system.
- It uses control systems and closed-loop data models.
- Products are highly customized.
3. The benefits of Industry 4.0
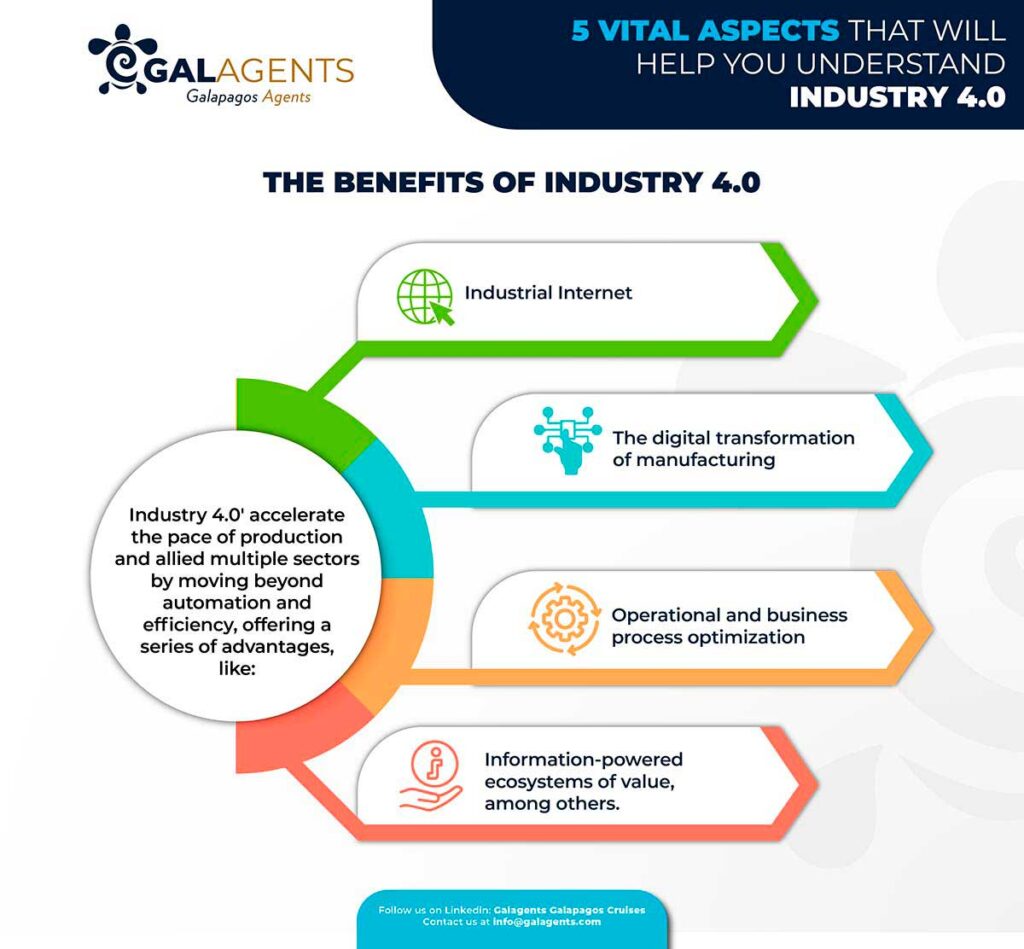
Industry 4.0′ primary objective is to accelerate the pace of production and allied sectors like logistics while identifying new business prospects and models by moving beyond automation and efficiency.
The majority of the advantages of Industry 4.0 are clearly, comparable to those of the Industrial Internet, the digital transformation of manufacturing, operational and business process optimization, and information-powered ecosystems of value, among others.
4. Six vital components that shape Industry 4.0
Let’s dig into the features that evolved and set up this 4th industrial revolution.
4.1. Internet of Things (IoT)
Machines on the manufacturing floor are outfitted with sensors with IP addresses, allowing them to communicate with other web-enabled equipment. Then, automation and connectedness allow vast volumes of essential data to be collected, analyzed, and transferred.
4.2. Cloud Computing
To fully implement smart manufacturing, the cloud makes the connectivity and integration of engineering, supply chain, production, sales and distribution, and service feasible, quick, and affordable.
4.3. AI and machine learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning may generate insights that provide visibility, predictability, and automation of operations and business processes—enabling manufacturers to thoroughly exploit the abundance of data created throughout the process, as well as by partners and third parties.
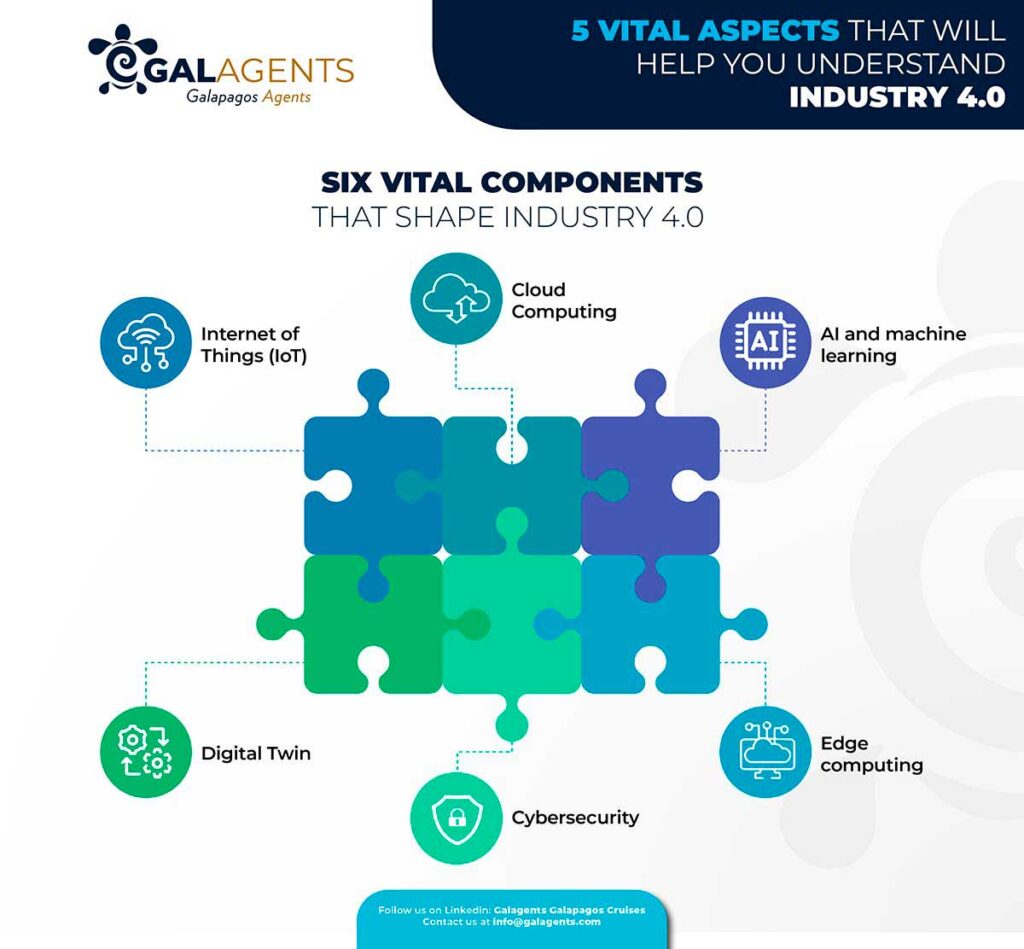
4.4. Edge computing
Real-time production processes require data analysis performed where the data is generated – at the “edge.” This reduces the time between when data is generated and when a response is required.
4.5. Cybersecurity
Manufacturing firms usually have not considered cybersecurity or cyber-physical systems. The same connection of operational equipment (OT) opens new entry points for unwanted assaults and viruses. Thus, a cybersecurity strategy is a must in Industry 4.0.
4.6. Digital Twin
Digital twins are a tool that manufacturers may employ to create new goods, streamline operations, and boost production by virtually cloning processes, manufacturing lines, factories, and supply networks through IoT sensors, gadgets, PLCs, and other internet-connected things.
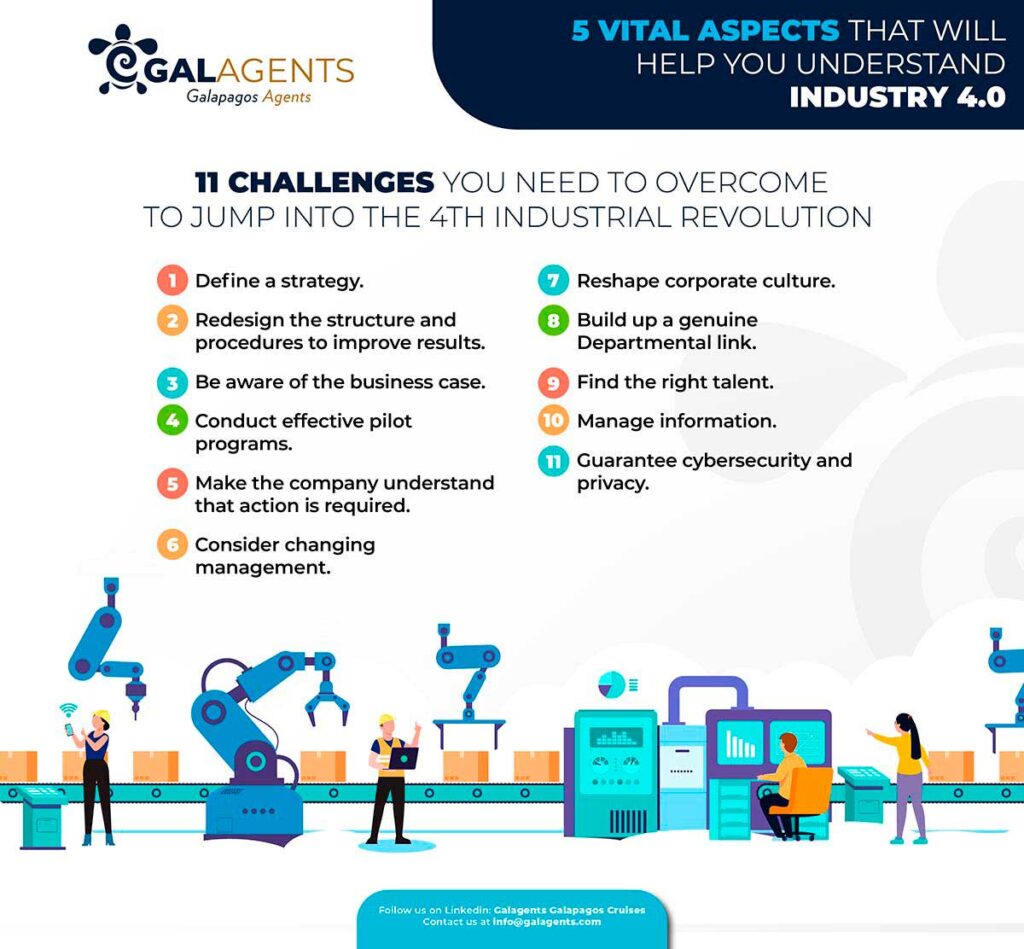
5. 11 challenges you need to overcome to jump into the 4th industrial revolution
- Define a strategy.
- Redesign the structure and procedures to improve results.
- Be aware of the business case.
- Conduct effective pilot programs.
- Make the company understand that action is required.
- Consider changing management.
- Reshape corporate culture.
- Build up a genuine Departmental link.
- Find the right talent.
- Manage information.
- Guarantee cybersecurity and privacy.
Download all the infographics here
As you’ve seen, the evolution of technology and communication, the need for customized products, and the escalation of businesses have pushed us to a new industrial revolution. A new industry that uses data to get valuable insights for decision-making, understanding customer needs, and improving and automating manufacturing processes.
How do you think this revolution is integrated into the tourism sector?
Sources:

