GALAPAGOS
ABOUT GALAPAGOS
They are located in the Pacific Ocean and have an extension from East to West of about 320 km. The equator line crosses the archipelago, specifically at the height of the Wolf volcano north of Isabela Island.
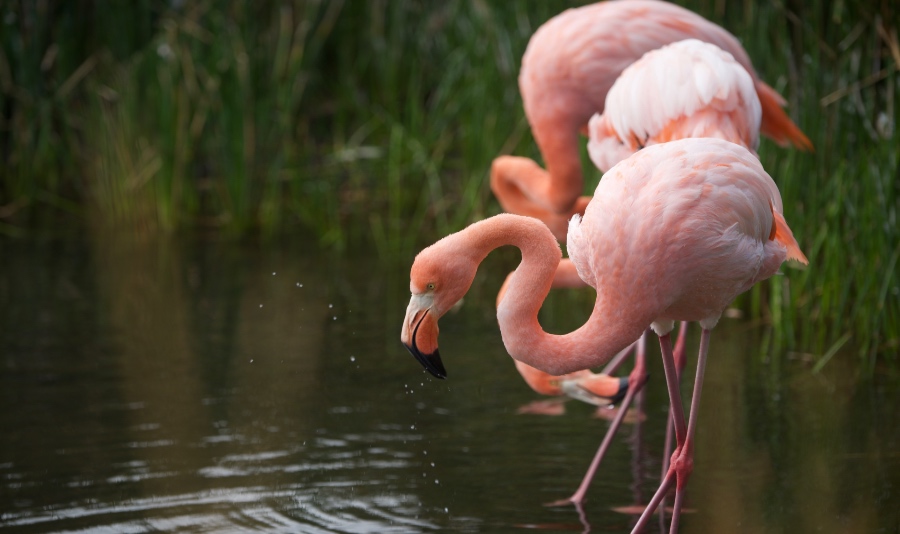
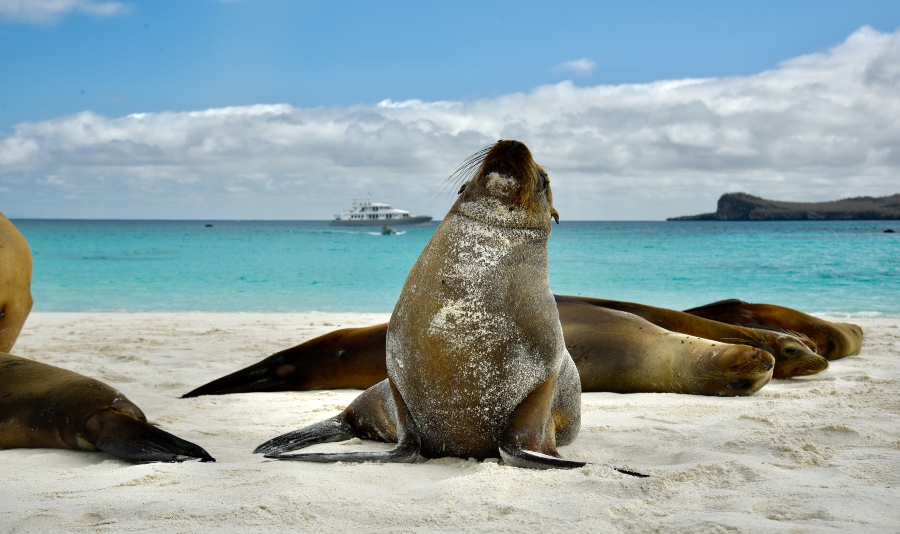
Because it is of volcanic origin, Galapagos has no connection to the South American landmass. They are built on a submarine basaltic plateau between 360 m and 900 m deep (1181 - 2953 ft). The Galapagos Islands are made up of 19 islands and 42 islets or rocks at an approximate age of 4 to 5 million. However, the islands have different periods of formation. For example, San Cristóbal is the easternmost Galapagos island and the oldest. Indeed, this island is the one that is approximately 1,000 km (621 mi) from the Ecuadorian coast. On the other hand, the most recent island is Fernandina, located further west of the archipelago and near the equator. Due to its rich biodiversity and fragility to human and climatic actions, the Galapagos Islands are considered one of the global biodiversity hotspots.
Because it is of volcanic origin, Galapagos has no connection to the South American landmass. They are built on a submarine basaltic plateau between 360 m and 900 m deep (1181 - 2953 ft). The Galapagos Islands are made up of 19 islands and 42 islets or rocks at an approximate age of 4 to 5 million. However, the islands have different periods of formation. For example, San Cristóbal is the easternmost Galapagos island and the oldest. Indeed, this island is the one that is approximately 1,000 km (621 mi) from the Ecuadorian coast. On the other hand, the most recent island is Fernandina, located further west of the archipelago and near the equator. Due to its rich biodiversity and fragility to human and climatic actions, the Galapagos Islands are considered one of the global biodiversity hotspots.


HISTORY - HUMAN
Many hypotheses said that ancient civilizations were among the first to discover and visit the archipelago, such as the Incas. Nonetheless, there is no written or archaeological evidence that proves these hypotheses.
Fray Tomas de Berlanga was the first to arrive on the islands on March 10, 1535. Then, by 1570, the cartographers Abraham Ortelius and Mercator included the Islands in a world atlas. There they called them "Insulae de los Galopegos."
Between the 16th and 18th centuries, the Galapagos Islands experienced a period of presence and dominance of French and English pirates.
It was Patrick Watkins in 1807 was the first settler in the Galapagos Islands, who was abandoned on Floreana Island. He survived by grewing potatoes and tobacco that later sold to passing ships.
In 1835 Charles Darwin, arrived to the Galapagos onboard the HMS Beagle, helping him to develop the Theory of Evolution for what he is famous for.
On September 8, 1978, the Galapagos Islands were the first site declared a Natural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO. By 1984, the archipelago was declared a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. On March 18, 1998, the Ecuadorian government created the Galapagos Marine Reserve, which expanded again in January 2022, reaching 198,000 km2.
Fray Tomas de Berlanga was the first to arrive on the islands on March 10, 1535. Then, by 1570, the cartographers Abraham Ortelius and Mercator included the Islands in a world atlas. There they called them "Insulae de los Galopegos."
Between the 16th and 18th centuries, the Galapagos Islands experienced a period of presence and dominance of French and English pirates.
It was Patrick Watkins in 1807 was the first settler in the Galapagos Islands, who was abandoned on Floreana Island. He survived by grewing potatoes and tobacco that later sold to passing ships.
In 1835 Charles Darwin, arrived to the Galapagos onboard the HMS Beagle, helping him to develop the Theory of Evolution for what he is famous for.
On September 8, 1978, the Galapagos Islands were the first site declared a Natural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO. By 1984, the archipelago was declared a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. On March 18, 1998, the Ecuadorian government created the Galapagos Marine Reserve, which expanded again in January 2022, reaching 198,000 km2.

